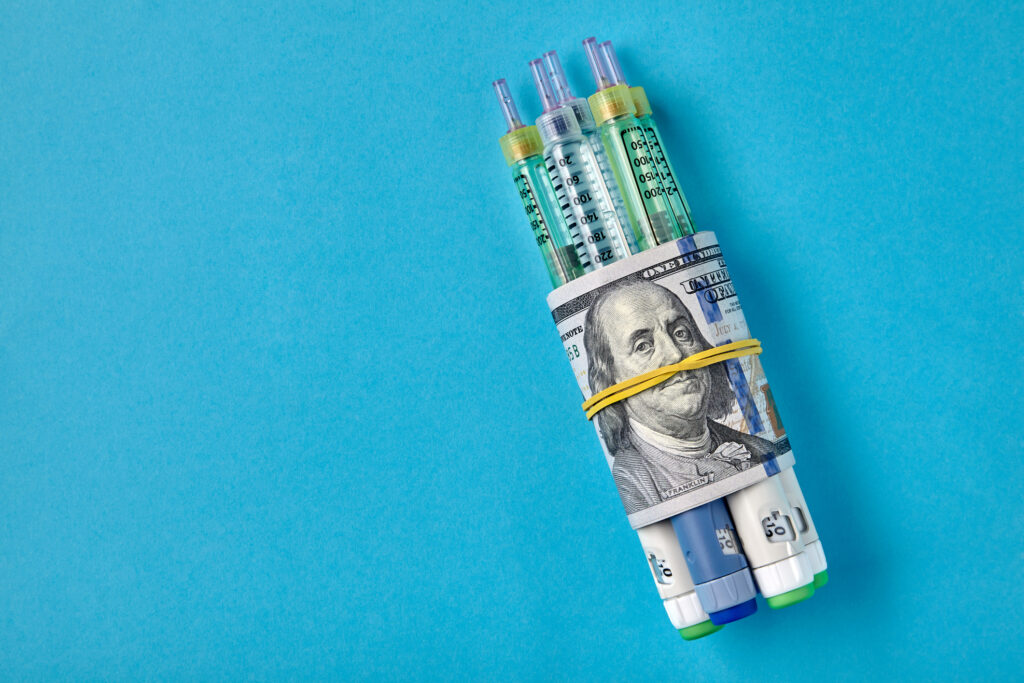

In 2022, DMGS discussed the surge in insulin prices, which had tripled from 2002 to 2013. This dramatic increase resulted in a corresponding tripling of patient insulin product prices. This upward trend has persisted, compelling certain patients to allocate over 40% of their post-subsistence family income solely to cover the cost of insulin. In response, many states have implemented caps and regulations to control insulin prices, mostly with $35 insulin price caps, or less. We revisit this topic to examine how states have continued their efforts to limit and regulate the escalating costs of insulin.
California Bill Sets New Guidelines for Insulin Prices
California State Senators Scott Wiener (D) and Susan Rubio (D) jointly introduced SB90 on January 17, 2023. The bill intends to reduce the costs for Californians with diabetes to obtain lifesaving and life-sustaining insulin. The bill would specifically ensure that a health care plan that is issued, amended, or renewed on or after January 1, 2024, shall not impose a copayment on an insulin prescription drug that exceeds thirty-five dollars ($35) for a 30-day supply, and shall not impose a deductible, coinsurance, or any other cost-sharing on an insulin prescription drug. The bill passed the Senate in late May 2023 and as of June 13, 2023, awaits further consideration in the Assembly.
Illinois State Senator Proposes Measures to Cap Insulin Drug Prices
Illinois State Senator Laura Murphy (D) introduced SB1559 on February 8, 2023. This proposed legislation, the Access to Affordable Insulin Act, would require the Public Health Department to create procedures and applications for insulin urgent-need programs. Additionally, the bill would require insurers to provide coverage for prescription insulin drugs as part of a health coverage plan to cap the maximum amount an insured individual must pay for a 30-day supply of covered prescription insulin drugs. Furthermore, it would cap the amount at $35, a reduction compared to the previous limit of $100. If approved, the legislation would take immediate effect.
Minnesota Bill Targets Capping Insulin & Asthma Pump Prices: Establishing Cost-Sharing Guidelines
Minnesota State Representative Michael Howard (D) introduced HB348 on January 17, 2023. The bill would establish cost-sharing limits for prescription drugs to treat chronic diseases. Under this legislation, the cost for each prescription drug, regardless of the amount or type of medication required, would be capped at $25 per one-month supply. Notably, this measure specifically targets the prices of insulin, asthma pumps, and epinephrine auto-injectors commonly used for allergies.
Rhode Island Bill Aims to Cap Costs for Insulin Administration and Glucose Monitoring Equipment
Rhode Island State Representative Brian Kennedy (D) introduced HB5281 on February 1, 2023. The bill’s objective is to cap the maximum payment for a 30-day supply of insulin administration and glucose monitoring equipment to $25 or for equipment designed to last more than 30 days without any deductible. If approved, the bill would go into effect on January 1, 2024. In March 2023, the Health and Human Service Committee recommended the bill be held for further study.
Latest News
Photo credit: iStock.com/naturalbox The debate over raw milk legislation has intensified in 2024, with several states introducing or passing bills that address the sale and distribution of unpasteurized dairy products. Raw milk has not undergone [...]
In this episode of the Back in Session podcast, hosts Ryan Stevens and Ryan DeMara sit down with Terra McClelland, President of the State Government Affairs Council (SGAC) and Vice President of Government and External [...]
Photo credit: iStock.com/Vladyslav Horoshevych Vaping has become increasingly popular among school-age Americans. A recent study found that 2.5 million U.S. youth vape. Relative to other nicotine products, young adults commonly prefer battery-operated devices like e-cigarettes, [...]
Photo credit: iStock.com/sittithat tangwitthayaphum State legislators have grappled with policies surrounding physicians offering life-ending care to terminally ill patients for many years. Life-ending care enables medical providers to go further than just making patients who [...]





Stay In Touch